Exploring AWS !!
Day 38:
Amazon RDS:
Check out Day 37 for Overview and advantages of RDS over deploying database on EC2.
RDS Backups:
- Backups are automatically enabled.
- Automated backups
- Daily full backup of database (during maintenance windows)
- Transaction logs are backed up by RDS every 5 minutes
- ability to restore at any point in time (from oldest to 5 mins ago)
- 7 days retention (increased to 35 days)
- Database snapshots:
Manually triggered by user
Retention of backup for as long as you want.
RDS — Storage Autoscaling:
- Helps increase storage on RDS database instance dynamically
- When RDS detects you are running out of free database storage, it scales automatically.
- Avoid manually scaling database storage
- You have to set the maximum storage threshold (max limit for database storage)
- Automatically modify storage if:
Free storage is less than 10% of allocated storage
Low storage lasts at least 5 mins
6 hours have been passed since last modification
- Useful for apps with unpredictable workloads
- Supports all RDS database engines (MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL server, Oracle)
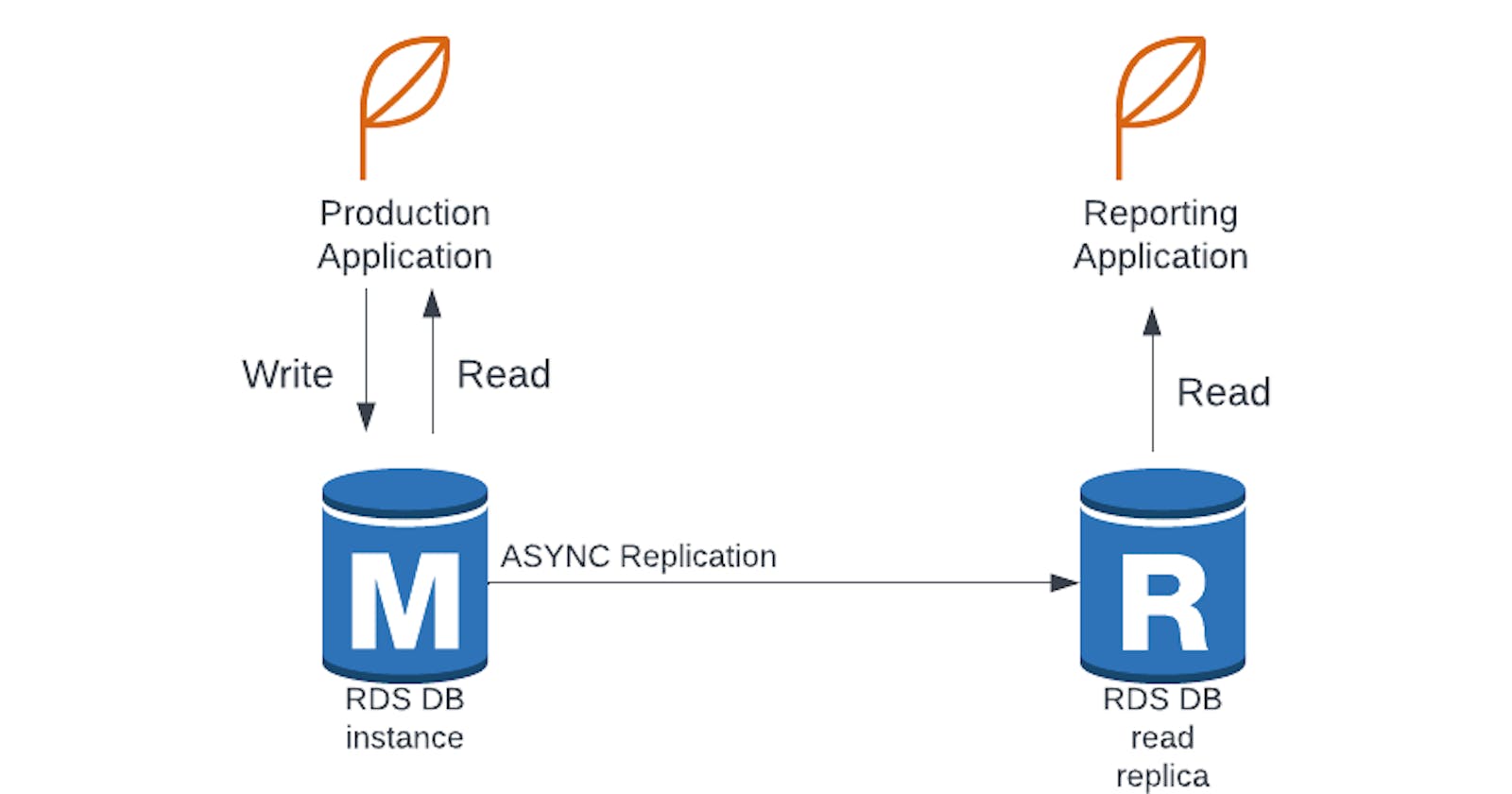
RDS Read Replicas for read scalability:
- can create upto 5 replicas
- within Az, cross Az or cross region
- Replication is Asynchronous, so reads are eventually consistent
- replication can be promoted to own database
- Application must update connection string to leverage read replicas.
Use Cases:
You have a production application that is taking on normal load.
You want to run a reporting application for running some analytics.
So, you create a read replica to run new workload there.
The production application is unaffected.
Read replicas are used for SELECT (=read) only kinds of statements (not INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE)

RDS Read Replicas — Network Cost:
There’s some network cost when data goes from one Az to another Az.
For RDS Read Replicas within same region, you don’t pay fees.
RDS Multi-AZ (Disaster Recovery):
- SYNC Replication
- One DNS name — automatic app failover to standby
- Increase availability
- Failover in case of loss of AZ, loss of network, instance or storage failure
- No manual intervention in applications
- Not used for scaling
Note: Read replicas can be setup as Multi-AZ for Disaster Recovery(DR).
RDS from Single AZ to Multi-AZ:
- Zero downtime operation (no need to stop database)
- Just click “modify” for database
- Following happens internally:
A snapshot is taken
A new database is restored from snapshot in a new AZ
Synchronization is established between 2 databases